Automotive Connectivity Technology
Connectivity technology evolved along with mobile phones, smartphones and PCs around us.
It is now introduced in many other equipment including digital cameras, home appliances, game machines, healthcare equipment and automobiles. Murata is now promoting and proposing solutions involving various connectivity technology applications under the slogan, "Let's have fun connecting the world!"
We would like to introduce automotive connectivity technology in this article.
Murata's Automobile Connectivity Modules
In terms of automotive connectivity modules, Murata released Bluetooth® modules (Fig. 1) for car navigation and car audio systems around 2003. These modules connect mobile phones and/or mobile music players wirelessly via Bluetooth® to realize the convenience of hands-free communication and music streaming inside the vehicle without affecting safety.
This Bluetooth® module includes software to support features such as hands-free communication, music streaming and transferring address book data, in addition to the hardware portion which fulfills wireless communication specifications defined by Bluetooth®. This software also supports features such as voice recognition allowing a driver to give verbal commands without affecting safety, echo canceller/noise reduction (EC/NR) for improving sound quality, and a function to improve interoperability (IOP) with many kinds of opposing devices.
Combo modules with added wireless systems such as WLAN, GPS and NFC in addition to Bluetooth® are being developed and commercialized recently (Fig. 2) . Murata provides total support (Fig. 3) for the WLAN system, currently the most promising system for automobile connectivity, including driver porting, system performance evaluation, a lineup of certified software, etc., drawing from the rich experience of manufacturing consumer connectivity modules.
As of December 2012, Murata has shipped over 13 million automobile connectivity modules to manufacturers all over the world.
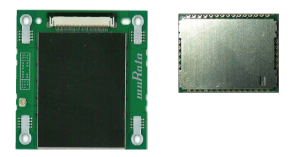
Fig. 1 Bluetooth® Module for Car Navigation and Car Audio Systems
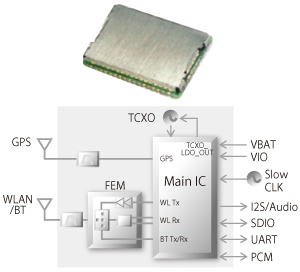
Fig. 2 Bluetooth®+WLAN+GPS Combo Module for Car Navigation and Car Audio Systems
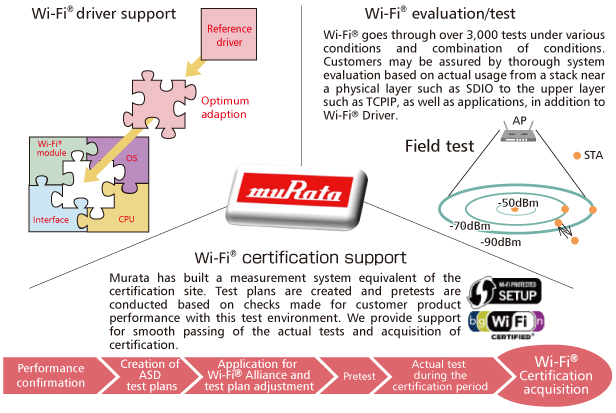
Fig. 3 Murata's WLAN System Total Support
Specifications Required for Automotive Components, and Murata's Initiatives
Compared with general consumer equipment, automobiles are used for longer periods and under severe environmental conditions. Since their use pertains to human lives and property, required specifications are naturally more stringent.
High reliability and availability are required for long-term, and zero-defect activities must be conducted over the product life of automobile connectivity modules as well, in addition to the realization of wireless features and performance. These requirements must be fulfilled by corresponding development, evaluation and manufacturing technologies.
During the development phase, we start out by carefully selecting devices to be used in the module. Murata supplies all sorts of electric components. With capacitors, Murata's mainstream products, we conduct all phases from material development to products shipment in-house.
Although many of the devices used in modules are manufactured in-house, devices made by our business partners (outside companies) are also in the picture. Our device selection process includes numerous meetings and discussions in order to make sure our device supplying partners understand Murata's concepts and requirements for automobile components. Our requirements include a fault analysis system and long-term availability in addition to the electronic and reliability performances of components.
Automobile-specific design rules, different from rules for consumer products, are established for the module design in order to ensure high reliability over a long term. These design rules allow for handling and inspection by automobile electrification manufacturers and ease of fault analysis, in addition to rules ensuring high reliability, such as specifications for component pitch and land patterns.
During the development evaluation phase, reliability as a module and wireless performance are evaluated. Modules must fulfill the requirement criteria from automobile electrification equipment manufacturers, as well as in-house evaluation criteria defined by accumulated experience and reliability engineering specialists. Evaluation periods for automobile modules are more than three times as long as that of consumer components. After coming up with a fine product design, manufacturing technologies to realize required performance and quality as well as stable and continuous production will be needed. Currently, Murata's connectivity modules including modules for automobiles are produced in-house. This is how we can build in quality to satisfy automobile specification from the beginning of the development phase.
Although production processes for automobile connectivity modules are essentially the same as consumer modules, we choose to produce the former on dedicated production lines. In order to achieve stringent automobile industry quality standards, assembly process, specialized inspection process and traceability are overseen by workers certified for automobile component material management and operations. Zero defect, a fundamental concept for manufacturing automobile components, is thus realized. The connectivity technology will expand its scope through the introduction of new wireless systems and new applications, thus making automobile components more multi-featured.
However, our basic philosophy and stance described in this article will be unchanged regardless of changes in products. We believe the final quality of components depends on our efforts to build in qualities faithfully and carefully, based on the fundamental philosophy of automobile components.
Glossary
*1 Bluetooth®:
It is one of the most popular short-range wireless communication technologies permeating the market along with mobile phones and mobile music players. Its communication range is about 10m.
*2 Opposing device:
An external device exchanging signals with the in-vehicle device
*3 Zero defect activities:
Continuous quality improvement activities to totally eliminate defects
Automobile Connectivity Technology of the Future
Connectivity technology will remain the key technology upholding the evolution of automobiles. Here, we introduce a few application examples (Fig. 4) .
Until recently, Bluetooth® was mainly used for transmitting sound in vehicles. Now smartphones are already beginning to come standard with a WLAN feature, enabling them to work together with WLAN-ready automobile equipment. Automobile equipment will be able to use external network through tethering, or take advantage of smartphone features directly.
We will be able to view streamed video clips as well. Other short-range wireless systems such as BLE (Bluetooth® Low Energy) and NFC (Near Field Communication) are also candidates for automobile connectivity.
BLE and NFC will eventually become standard features of smartphones. A driver's smartphone may be able to function as a key for automobiles, unlocking the door and automatically adjusting the steering wheel and seat positions as the driver approaches the vehicle.
NFC, a technology used for "wallet phones" and "Mobile Suica®," is now considered for various authentication applications including in-vehicle pairing of Bluetooth® and WLAN. In addition to infotainment applications described thus far, these wireless technologies are also considered for easing traffic congestion and promoting safety through vehicle-to-network, vehicle-to-vehicle or road-to-vehicle communications. Furthermore, simplification of very complex wired in-vehicle harnesses offering multiple features with the wireless connection may become future considerations.
Automobile applications are truly diverse, ranging from infotainment to the safety of "driving, turning and stopping." Although we continue to make more critical safety features wireless, and will require further breakthroughs, automotive connectivity technology holds limitless potentials.
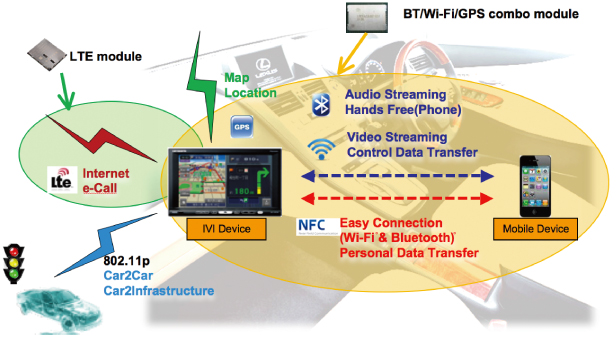
Fig. 4 Implementation Examples for Automobile Wireless Connectivity
Final Remark
Under the slogan "Let's have fun connecting the world!" Murata has dealt with many kinds of wireless systems offering connectivity technology-based solutions for numerous equipment around us. Through our actions, we have formed a base technology to contribute to the advancement of automobile connectivity. Murata will continue to provide optimal automobile connectivity solutions to the market in a timely fashion. In the near future, we will propose attractive total solutions combining other unique in-house technologies and components that are already utilized as automobile components including sensor devices.
Glossary
*4 Tethering:
Connecting with external networks such as Internet using a communication terminal like a smartphone as an external access point
*5 Bluetooth® Low Energy:
It is a new wireless standard added by Bluetooth® version 4.0. Although it is not compatible with previous Bluetooth®, it can communicate at 1/10 to 1/20 energy consumption. Depending on the compatibility, devices complying with this standard are given either Bluetooth® Smart or Bluetooth® Smart Ready logo.
*6 Infotainment:
A term made up by connecting "information" and "entertainment," representing entertaining information services