Surface Mountable Accelerometer Device for Tire Pressure Monitoring
Systems
Tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) are placed under a spotlight worldwide, especially in Europe and
the United States, for their ability to protect drivers against danger by monitoring tire pressure, while
being environment friendly. Murata's surface mountable accelerometer devices (shock sensors) have become an
essential component for TPMS. In this article we will introduce the features and roles of surface mountable
accelerometer devices.
What Is TPMS?
A TPMS is mounted inside the tire valve, measures tire pressures and temperatures with a pressure sensor
and a temperature sensor and sends their status to a receiver in vehicle via wireless communication. If
any abnormality is detected in tire pressure or temperature, information is displayed on the instrument
panel to warn the driver.
Use of TPMS is rapidly expanding globally and was mandated from September 2007 in the United States, from
November 2012 in Europe, and January 2013 in Korea. It is rumored that they will be mandated in Japan and
China as well in the near future. TPMS will continue to be a part of our daily lives.
TPMS was developed to improve automotive safety while vehicles are in motion, after an investigation of a
series of accidents caused by tire bursts due to low tire pressure in the United States took place during
2000. It was found out later that TPMS is an ecological and environment-friendly technology contributing
to energy saving and CO2 reduction from improved fuel efficiency by helping maintain proper tire pressure.
It further contributes to environment by extending the life of tires through proper tire pressure
maintenance, consequently reducing use of resources as well as waste. The market for TPMS will continue to
grow due to improved safety and environment friendliness from their use.
What Is a Surface Mountable Accelerometer Device?
Surface mountable accelerometer devices (shock sensor, Fig. 1) are a type of accelerometers using
piezoelectric ceramics.
Piezoelectric ceramics (barium titanate, lead zirconate titanate, etc.) are ceramics that generate
electric energy when pressure is applied (piezoelectric effect) and ceramics that generate mechanical
strain when electric energy is applied (inverse piezoelectric effect) . Their excellent features are high
electromechanical conversion efficiency, relatively free configuration, flexible characteristics and ease
of mass production. Piezoelectric ceramics are widely used for ultrasonic sensors and other sensors in
addition to accelerometers.
We call accelerometers with especially high resonant frequencies (over 20kHz approximately) , enabling
them to detect rapid acceleration, surface mountable accelerometer devices. On the other hand, they are
not suitable for detecting smooth accelerations such as a free fall by the force of gravity. They have a
sandwich construction with substrates sandwiching a device (piezoelectric ceramic) from top to bottom
(Fig. 2) . When this device receives a shock (acceleration) , the ceramic inside deforms, generating
electric energy from the piezoelectric effect, to communicate information regarding the detected shock to
the equipment. Their detection capabilities range from a small shock a human body receives while walking,
to a big shock from an automotive collision, allowing for various applications.
Fig. 1
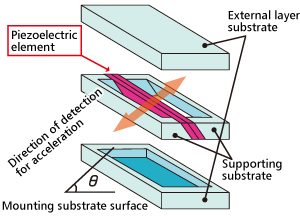
Fig. 2
Features of Surface Mountable Accelerometer Device
There are three major features for Murata's surface mountable accelerometer device.
Small size and low profile
Murata's smallest surface mountable accelerometer device currently used for TPMS is 4.8 x 2.3 x 1.3mm.
This size is mountable in TPMS, which is currently going through rapid downsizing.
High reliability
Since surface mountable accelerometer devices for TPMS are mounted inside tires, they are capable of
withstanding stringent conditions such as vibration from rough road surface, a wide range of
temperatures from below freezing point to a near 100°C, as well as high humidity near 100%.
Flexible detection angles
Optimal angles for shock detection by surface mountable accelerometer devices differ depending on the
direction of the device. Murata makes surface mountable accelerometer devices with various detection
directions available. Customers may select ideal sensors according to their specifications (Fig. 3) .
Fig. 3: Lineup of surface mountable accelerometer device for TPMS
Lineup of surface mountable accelerometer device for TPMS
Roles Surface Mountable Accelerometer Devices Play
Initially used for airbags, surface mountable accelerometer device applications for automobiles are
expanding especially for TPMS. We will probably see TPMS installed in Japanese cars in the near future.
What kind of roles, then, do surface mountable accelerometer devices play in TPMS?
As mentioned before, TPMS was originally developed to improve drivers' safety. In that sense, TPMS does
not play a vital role while the car is stopped, or actually wastes energy if it stays active.
By mounting a surface mountable accelerometer device, TPMS can operate only when there is more than a
certain amount of shock (Fig. 4) . Energy consumption for data-transmitting wireless communication
circuits can especially be reduced by limiting tire pressure detection and pressure data transmission only
while in motion. This feature, to power the equipment only during operation and keep them in the sleep
mode automatically while not in operation, is called "wake-up"feature
*1, contributing to significant power saving in the equipment.
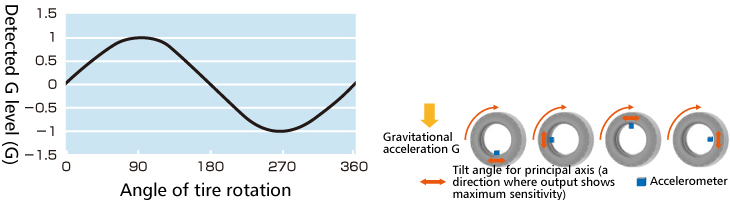
Fig. 4 Tire rotation and sensor output
In addition to the surface mountable accelerometer device-based wake-up feature for TPMS market, there is
also a semiconductor MEMS-based*2 (micro electro
mechanical systems) wake-up feature, and two of them together comprise the majority share of the market.
Since current TPMS are powered by batteries that are required to last between a few years to 10 years, low
power consumption is a very important requirement by TPMS manufacturers.
Also the mounting position of TPMS being inside tire valves requires very high reliability. Murata's
surface mountable accelerometer device satisfies both low power consumption and high reliability
requirements and commands over 50% share of the market currently. Although the wake-up feature with the
surface mountable accelerometer is currently only implemented in TPMS, as the low power consumption trend
continues, there will be other situations where surface mountable accelerometer devices can play a role in
the future. They may include sensing applications such as a building and energy management system (BEMS*3) , a home energy management system (HEMS) , servers to archive data from BEMS and HEMS, home electrical appliances and
mobile terminals.
Future of TPMS
TPMS is becoming smaller as with many other electronic equipment in the market. The largest
advantage to downsizing TPMS is tire balance. As described earlier, TPMS are mounted inside tire
valves, and the larger they are the more they would affect the tire balance. Therefore, we can
predict that TPMS will continue to downsize, and surface mountable accelerometer devices will be
required to downsize while maintaining the current level of reliability.
What will happen next, if surface mountable accelerometer devices become smaller? It is conceivable
that TPMS will be mounted directly to the tire itself (in tire treads) to transmit warnings to
drivers more directly and precisely for improved safety (Fig. 5) . This way, TPMS will able to
immediately warn the driver of dangers based on information such as abnormalities caused by bumpy
unpaved roads, road surface temperature approaching 100°Cfrom the summer sun and frozen ground
of the winter.

Fig. 5
Smaller size and higher reliability will be required for TPMS mounted in tire tread, compared with
valve-mounted TPMS. Since semiconductor MEMS are not very strong against temperature changes, we will need
to keep proposing surface mountable accelerometer devices to our customers.
We will continue to help make TPMS smaller and lower profile, by coming up with total solutions through
utilization of Murata's module technology combined with other sensor technologies such as pressure
sensors.
Final Remarks
In the light of environmental issues such as advancing global warming, initiatives to save energy are
conducted throughout the world. As Kyoto Protocol was extended until the end of 2020, requirements and
interests for energy saving will become stronger for sure.
Murata's surface mountable accelerometer devices have a potential of contributing to energy saving for
many types of equipment in addition to TPMS. It is Murata's wish to continue being a supplier that can
propose attractive features to our customers and end users at all times, in terms of performance and
environment friendliness.
Glossary
*1 Wake-up feature:
In this article, a wake-up feature indicates a feature to switch between normal mode and low power
consumption mode (reduced RF communication cycles while tires are not in motion) .
*2 MEMS:
A device that integrates electronic components such as sensors, and an electronic circuit on one
substrate
*3 BEMS and HEMS:
A management system to control building equipment and curb demand peaks by measuring and storing energy
in homes and buildings