Figure 4 shows the Murata Bluetooth® low energy module integrated into the ring pulse meter. This module includes a “protocol stack,” software required for wireless communication, which makes it possible to design Bluetooth® low energy-based equipment easily without special knowledge about the communication standards. The integral antenna chip in the module eliminates the need to design a wireless circuit into the equipment.
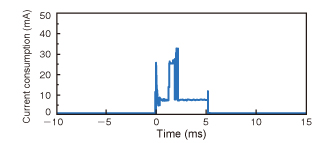
Figures 5 and 6 show Bluetooth® low energy module current consumption in the ring pulse meter. High peaks of approximately 30mA are caused by wireless communication. Once every 200ms, the module transmits 3 bytes of data (the overall length of the packet including the header is 20 bytes). Low peaks of approximately 7mA are caused by communication with the PPG sensor. For most of the time during which a connection is maintained, the module is in sleep mode, keeping mean power consumption at low levels. With the Murata prototype, measurements show that the Bluetooth® low energy module has mean current consumption of approximately 350µA. The small rechargeable battery has a capacity of 70mAh. Assuming that the module alone uses the entire capacity, it can, therefore, operate continually for about a week.
Connecting various healthcare devices to the network via TV or mobile phone as gateways opens the possibility for further applications. By unifying measured data and coordinating with health consultation services, for example, it becomes possible to apply this technology in the prevention of chronic disease and in facilitating remote medical care. Such new uses serve to improve quality of life.
Wireless healthcare equipment, which allows measured data to be transmitted to PCs and mobile phones without complicated wiring, is opening up a promising market. Bluetooth® low energy is particularly beneficial where mobile phones are used as a gateway. Murata is commercializing Bluetooth® low energy modules as tools for linking healthcare devices with networks. The aim is to make healthcare devices ? such as bathroom scales, blood pressure monitors, and heart rate meters ? more familiar to consumers.
Fig. 6 Current consumption waveform (closer view of wireless communication)
The Bluetooth trademark is owned by Bluetooth SIG, Inc., USA. Wi-Fi and ZigBee are (registered) trademarks of Wi-Fi Alliance and ZigBee Alliance, respectively.